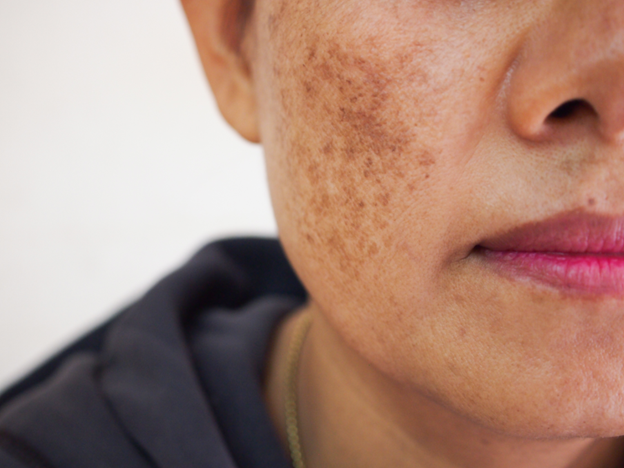
Melasma is a common skin condition that many people grapple with. It’s characterized by noticeable brown or blue-gray patches that appear mainly on the face. While some people worry about its appearance, it’s important to understand that melasma is not dangerous. We’ll dive into the details of this condition, tackle common misconceptions, and offer insights into its causes, symptoms, and management strategies.
Demystifying Melasma: A Closer Look
Melasma, often linked to hyperpigmentation, occurs when skin cells produce too much color. This overproduction leads to uneven patches on the skin. While melasma itself isn’t harmful, it is very common. People affected by it have brown or blue-gray marks that can vary in shape and size. Often appearing in symmetrical patterns, these patches can appear on both sides of the face, adding to the stress for many who value even skin tone.
Understanding Melasma’s Nature:
- Melasma is a type of skin discoloration.
- It arises from the overproduction of pigment in skin cells.
- Though it’s not a health risk, it can affect appearance.
- Visible as brown patches, it commonly affects the face.
- Knowing about melasma can help in seeking the right care.
Identifying the Different Types of Melasma
There are three main types of melasma: Epidermal, Dermal, and Mixed. Each type has distinct characteristics:
- Epidermal Melasma: This type appears in the outer layers of the skin and is lighter in color.
- Dermal Melasma: Found in deeper layers, these patches are darker and often blue-gray.
- Mixed Melasma: This type combines both epidermal and dermal traits, making diagnosis a bit more challenging.
Understanding these differences is crucial as it guides treatment options suited to each type.
Detecting Melasma Patterns and Locations
Melasma presents in different patterns and locations, mainly on the face:
- Centrofacial: Found on the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin.
- Malar: Present on the upper cheeks.
- Mandibular: Focused along the jawline.
- Extra-facial: Although less common, it might affect arms or neck.
Knowing these patterns helps in identifying melasma and its treatment options.
Who is Affected by Melasma?
Melasma is more common among women than men and often seen in people with a darker skin tone. Pregnancy is a known trigger because hormonal changes can spark melasma. Women with a family history, or those taking hormone medications, might see a rise in melasma cases. While age isn’t a direct factor, changes in hormonal levels during certain life stages, like pregnancy or menopause, can increase the chances of developing melasma.
Exploring the Causes and Triggers of Melasma
One of the main triggers of melasma is exposure to UV light. Sunlight can make the patches darker and more noticeable. Aside from sunlight, hormonal changes, such as those seen during pregnancy or due to birth control pills, can also trigger this condition. Genetic factors, too, play a part. While certain lifestyle habits, like an unhealthy diet or stress, might not directly cause melasma, they can worsen it.
How is Melasma Diagnosed?
Melasma is primarily diagnosed through visual examination by a dermatologist who can recognize its distinct patterns. Sometimes, a Wood’s lamp is used, a tool that offers a closer look at discolorations. This helps in distinguishing melasma from other skin pigmentation issues. Accurate diagnosis ensures that the treatment plan addresses the right condition.
Effective Treatment Options for Melasma
Treating melasma often starts with simple, non-invasive methods:
- Sun protection: Wearing sunscreen daily is crucial.
- Topical creams: These can help lighten the patches.
- Chemical peels: These treatments aid in removing discolored skin layers.
- Laser therapies: An advanced option aimed at significant reduction of skin patches.
Each method comes with pros and cons. For instance, while creams are easy and convenient, they may take longer to show results. Laser therapies promise quicker results but can be costly and sometimes cause side effects like redness.
Daily Management and Living with Melasma
Daily care and protection can play a big part in managing melasma. This includes:
- Wearing broad-spectrum sunscreen every day.
- Using hats and clothing for additional sun protection.
- Embracing a skin-friendly diet.
On a psychological level, melasma may affect self-esteem. Practical tips include using makeup to camouflage spots and build confidence. Being aware of melasma’s chronic nature helps in sustaining a long-term care strategy.
Proactive Prevention Strategies and Lifestyle Tips
Keeping melasma at bay requires commitment to prevention:
- Regular use of sunscreen and protective clothing.
- Maintaining a skin-friendly lifestyle, such as minimizing sun exposure.
- Monitoring hormones and adopting a consistent skincare routine is beneficial.
Conclusion: Navigating Life with Melasma
In summary, understanding melasma is the first step in addressing its impact. With the right care, it’s possible to effectively manage and live life to the fullest. Regular consultations and being proactive about skin health can ensure that melasma remains a small concern in the larger scope of one’s life. Taking charge with daily sun protection and self-care strategies can help keep melasma’s effects at bay, giving you the confidence to face the day.